Vote for only one
No runoff
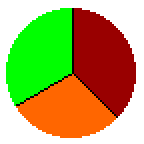
If n ≥ 3, then fails: the vote
favors most different candidate
Favors extremist candidates
Vote for only one
Runoff if all < 50%
If n ≥ 4, then fails: the vote
favors most different candidate
Runoff disenfranchises losing parties
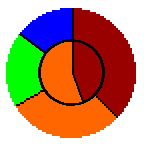
Vote for any you like
No runoff
Voters have unequal power
Favors centrist candidate
Expect numerous recounts
Vote for any you like
Runoff if all < 50%
Voters have unequal power
Favors centrist candidate
Runoff disenfranchises losing parties
Score = sum of votes.
If none > 50%, best 2 get plurality runoff.
Score = sum of votes.
If none > 50%, best 2 get plurality runoff.
(Orange and green on chart split vote)
(Green on chart removed)
Almost all elections will have recounts
(Green on chart removed)
Rank your choice order
No runoff
Can't tell likes from dislikes
Can't favor or disfavor equally
Your vote can elect a dislike
Rank your choice order
Round: remove low if all < 50%
Runoff rounds destroy votes
Can't tell likes from dislikes
Your vote can elect a dislike
Vote on each choice separately
Score =
YES sum −
NO sum
Many abstains cause surprise win
Voting Plurality causes errors
All negative scores cause revote
Rate choice separately −5 .. +5
Score = sum of ratings
Voters have unequal power
Favors centrist candidate
Expect numerous recounts
Scoring systems used differ
If all < 50%, lowest choice eliminated
Score = YES − NO. Blank = Abstain.
Rate from −5 to +5 (or −50 to +50)
The vote on B (orange) is same for both.
Order of NO votes can help elect a NO.
Don't vote Abstain except for lower YES.
Almost all elections will have recounts
Votes for all candidates of one party
Discriminates against lower candidates.
Fills m seats in one race
Usually all seats m are the same party
Finds winner using normal voting
Then makes all votes for the winner
Removes candidates from the race
Some states remove parties instead
in the party of a favorite candidate.
of the same party.
votes into votes for the winner.
candidates or parties from the race.